Mitsubishi 6 Hp 4 Stroke Engine Manual
. OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL 10 The operator and supervisor are requested to read this Oper- ation and Maintenance Manual carefully before operating the engine or conducting inspection and maintenance. Never operate the engine or conduct maintenance work with- out completely understanding this manual. July 2009 Pub. INTRODUCTION This operation and maintenance manual contains detailed operation, inspection and maintenance information for engines from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Please read this manual thoroughly before proceeding with operation, inspection, and maintenance work for correct use and servicing. Failure to follow directions in this manual may result in serious accidents.
FOREWORD Limited warranty Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Solution manual project economics and decision analysis. Will repair or replace parts returned to us when we judges that the parts are defec- tive in material and/or workmanship after conducting inspection. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.' S warranty is limited to the compensation work of repair or replacement of parts. Protection Agency.
Warranty coverage Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Warrants to the first owner and each subsequent purchaser of a new non-road die- sel engine that the emission control system of your engine: is designed, built and equipped so as to conform at the time of sales with all applicable regulation of the U.S. Envi- ronmental Protection Agency.If the vehicle in which the engine is installed is registered in the state of California, a.
MANUFACTURER'S WARRANTY COVERAGE: The 2008 and later heavy-duty off-road engines are warranted for the Warranty Period. If any emission-related part on your engine is defective, the part will be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. OWNER'S WARRANTY RESPONSIBILITIES: As the heavy-duty off-road engine owner, you are responsible for the performance of the required maintenance. Subsection (e) shall be warranted for the warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2). If any such part fails during the period of warranty cove rage, it shall be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. According to Subsection (4) bel o w. Any such part repaired or replaced under the war- ranty shall be warranted for the remaining warranty period.
Heavy Industries, Ltd. Shall not be liable to warrant failures of warranted parts caused by the use of a non- exempted add-on or modified part. (11) The Air Resources Board may request and, in such case, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Shall provide, any documents which describe that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'
S warranty procedures or policies. (F) Any other part with the primary purpose of reducing emissions or that can increase emission during fail- ure without significantly degrading engine performance. (e) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Shall furnish with each new engine written instructions for the maintenance and use of the engine by the owner. If you lost or damaged this manual, obtain a new tors.Also add safety, caution and operating signs that describe the original warning label statements in the copy at a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Native language of the operators. As soon as possible.
FOREWORD Warning indication The following means are used to call the attention of the operators and maintenance personnel to potential dangers of the engine. Warning statements in the manual Warning labels affixed on the engine Warning statements The warning statements in this manual describe potential danger in operating, inspecting or maintaining the engine, using the following 5 classifications to indicate the degree of potential hazard. FOREWORD Units of measurement Measurements are based on the International System of Units (SI), and they are converted to the metric system units in this manual using the following conversion rates.
Pressure:1 MPa = 10.197 kgf/cm Torque:1 Nm = 0.10197 kgfm Force:1 N = 0.10197 kgf Horsepower:1 kW = 1.341 HP = 1.3596 PS Meter of mercury:1 kPa = 0.75 cmHg. CONTENTS Avoid immediate restart after abnormal stop.1-5 Chapter 1 Avoid continuous engine operation at low oil BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS pressure.1-5 Fire and explosions.1-1 If belt breaks, stop engine immediately. 1-5 Keep flames away.1-1 Service battery.1-6 Keep engine surrounding area tidy and clean. CONTENTS Chapter 3 Chapter 6 OPERATION COOLANT Preparations for operation.3-1 Recommended water for coolant.6-1 Long life coolant (LLC).6-1 Engine external - Inspect. 3-1 Battery electrolyte level - Inspect. 3-1 Genuine LLC.6-1 Fuel tank oil level - Check.
3-2 Other brand LLCs. Fuel tank - Drain water.8-2 General precautions.11-1 Solenoid fuel pump filter - Inspect and clean. 8-2 Contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Fuel system - Bleed air.8-3 Industries, Ltd. For repair service.11-1 Water sedimenter - Drain water. 8-5 Considerations before work. CONTENTS Fig. 8-13 Oil filter - Change.8-9 List of illustrations Fig.
2-1 Engine left view.2-1 Fig. 8-14 Oil filter.8-9 Fig. 2-2 Engine right view.2-1 Fig. 8-15 Radiator filler cap.8-10 Fig. 2-3 Engine left view.2-2 Fig.
CONTENTS List of tables Table 3-1 Preheat duration (automatic grow plug).3-4 Table 3-2 Preheat duration (manual grow plug). 3-4 Table 3-3 Standard values at rated speed. 3-6 Table 4-1 Recommended limit and use limit of fuel property. 4-2 Table 5-1 Engine oil properties. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Fire and explosions Keep flames away Use explosion-proof lighting Do not use flames near the engine (in apparatus the engine room).
Fuel vapor or other When inspecting fuel, engine oil, coolant, battery elec- gas can catch fire and produce dan- trolyte, etc., use a flameproof light. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Stay clear of all rotating and moving parts Install protective covers around Lockout and tagout rotating parts Be sure to lockout and tagout before starting inspec- Make sure the protective covers of tion and maintenance. The engine are correctly installed. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Be careful of exhaust Be careful of falling down fume poisoning Lift engine carefully To lift the engine, use slings capable Operate engine in a well-venti- of supporting the weight of the lated area engine. If the engine is installed in an Attach the wire rope to the hangers enclosed area, and the exhaust gas. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Protect ears from noise Be careful of burns Wear ear plugs Do not touch the engine during Always wear ear plugs when entering or immediately after operation the machine room (engine room).
To avoid burns, do not touch the Combustion sound and mechanical engine during or immediately after noise generated by the engine can. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Be careful when handling When abnormality occurs fuel, engine oil or LLC Do not add coolant immediately after a sudden stop due to over- Use only specified fuel, engine heating oil and LLC If the engine stops suddenly or if you have no choice Use fuel, oil and LLC specified in this manual, and but stop the engine suddenly due to overheating, do handle them carefully.
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Service battery Handle the battery correctly Never use flames or allow sparks to generate near the battery. The bat- tery releases flammable hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Any flames or sparks in the vicinity could cause an explosion. If there is a need to modify the engine, contact a Failure to conduct the specified inspections may dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Cause various engine problems, damage to parts, and Observe safety rules at work serious accidents. Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Conduct cooling operation Use of tools optimum for each before stopping the engine work Before stopping the engine, let it idle in low gear for 5 Always keep in mind to select most appropriate tools to 6 minutes to cool down. Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS Engine external diagrams The external diagram is for the standard type of the engine.
The installed equipment and shapes differ according to the engine type. L2E left view Thermostat Oil filler Exhaust manifold Rear hanger Alternator Front Rear. Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS L3E left view Oil filler Rear hanger Thermostat Exhaust manifold Alternator Front Rear Starter Belt Flywheel Oil pan Fig.
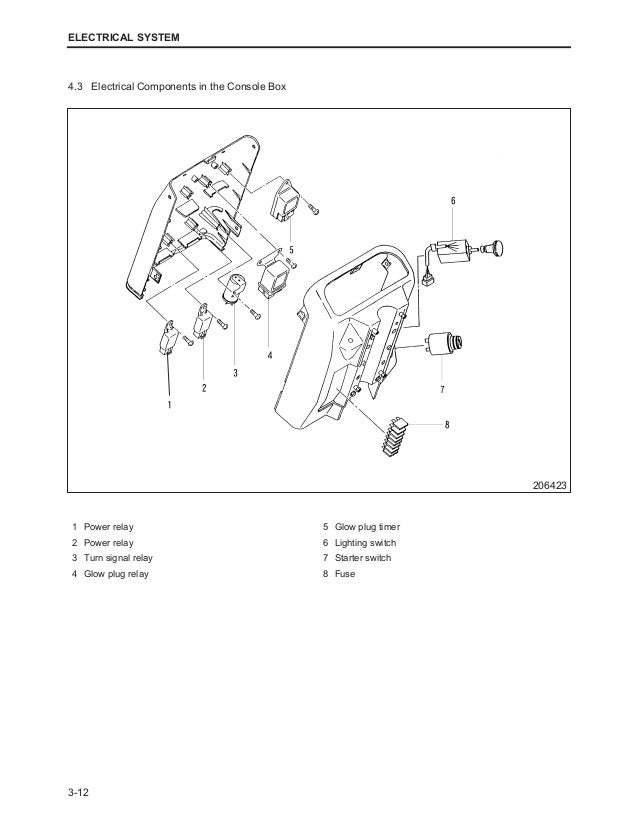
2-3 Engine left view L3E right view Fuel injection nozzle Front hanger Inlet cover Fuel injection pump Stop solenoid Fuel filter Water pump. Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS Equipment and instrument The installed equipment and shapes differ on the engine type. Starter switch The starter switch is used to start the engine.
HEAT HEAT When the key is turned to this position, the glow plugs START become hot and allow easy startup of a cold engine. Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS Water temperature meter and thermo unit The engine coolant temperature detected by the thermo unit is displayed by the water temperature Thermo unit meter. When the water temperature meter shows 95°C 203°F, idle the engine in low gear until the tempera- ture becomes normal.
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS Stop solenoid The stop solenoid operates for normal shutdown of engine operation. The stop solenoid moves the rack of fuel injection pump to cut the fuel, and consequently stops the engine. Two types of stop solenoids are available. RUN OFF (ETS: Energized To Stop) type Not energized while the engine is running.
Stop the engine if the protection device is activated, investigate the cause of abnormality and restore it. When the cause of abnormality is unknown, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. The installed protection devices, type (set value) or shapes varies according to the specifications. Preparations for operation Should an engine abnormality be observed during operation, stop the engine and correct the problem, or contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Always conduct the following inspection before starting the engine. Engine external - Inspect Be sure to keep combustible materials away from the engine, especially from the hot engine parts such as exhaust manifolds, or the battery. Chapter 3 OPERATION Fuel tank oil level - Check When working around fuel, make sure there are no open flames, heaters or other fire hazards. Wipe off any spilled fuel completely.Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire. Do not remove the strainer when filling the fuel tank. For fuel to be used, refer to 'FUEL'. Chapter 3 OPERATION Coolant level - Check Stand the lever to Turn the cap about Remove the radiator filler cap only after the engine the upright position half a turn has cooled to room temperature.
Place a waste cloth over the cap, and loosen the cap about a half-turn or stand the lever to the upright position to release inter- nal pressure. Chapter 3 OPERATION Starting The starting method changes based on the application and specifications.Start the engine according to the specified procedure.
Before starting the engine, check to make sure no one is near the engine and that tools are not left on or near the engine.In a loud voice, notify people in the area when starting the engine. Chapter 3 OPERATION Warm up operation Do not approach rotating parts during operation. Entanglement by rotating parts can cause serious injury. After the engine starts, operate the engine in a no load condition at low idling speed for 5 to 10 minutes to warm up the engine. Chapter 3 OPERATION Operation Cautions when operating Inspection during operation Carefully check the exterior of engine such as piping joints for leaks. Do not approach rotating parts during operation. Check for abnormal engine noises or vibrations such Entanglement by rotating parts can cause serious as knocking.
Engine stopping method may differ depending on the specifications. Follow the instructions according to the specifications of the equipment. Inspection after stopping Inspect the engine for fuel, oil or coolant leakage.
If any leakage is found, repair the leakage or contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Chapter 4 FUEL Recommended fuel Use a fuel specified in this manual only. Do not refill the fuel tank more than the specified level, as it may Diesel fuel result in a fire. Equivalent Use a diesel fuel equivalent for 'JIS K 2204 diasel fuel'.
Chapter 4 FUEL Table 4-1 Recommended limit and use limit of fuel property Properties Recommended limits Use limits Test method JIS K 2265:2007 Flash point 50°C 122°F or higher 45°C 113°F ISO 3769 ISO 2719 Initial boiling point 170°C 338°F or higher JIS K 2254:1998 Distillation. Chapter 4 FUEL Table 4-1 Recommended limit and use limit of fuel property Properties Recommended limits Use limits Test method Foreign materials JIS B 9931:2000 (foreign materials at engine fuel 5.0 mg/liter or less ISO 4405 inlet) Lubricity: MWSD (Measured mean 460 μm 0.02 in. or less Wear Scar Diameter) by HFRR (calculated wear scar diameter.
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL Recommended engine oil Use only the engine oils recommended in this manual. Never use other oils. The use of inappropriate or inferior oils will result in sticking of piston rings, seizure between piston and cylinder, or premature wear of bearings and moving parts, and significantly shortens the service life of the engine. Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL Abrasion powder in the engine oil also accelerates Engine oil performance deterioration as it can catalyze oxidation reaction. Requirements Dust and dirt entered from outside deteriorate the en- Engine oil requires the following performances. Gine oil as well.
Contamination and deterioration pro- Excellent dispersion performance (the ability of oil to cess accelerates with operation time. Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL Definition of properties of engine oil Viscosity Water content Viscosity is a basic physical property of engine oil and Water in oil promotes corrosion/wear, and decreases is considered as the most important aspect when eval- lubricity in sliding parts. Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL Service Limits of engine oil Engine oil degrades through the use and by lapse of time.
To determine the timing of engine oil replacement, analyze the used oil, and understand the condition of oil deterio- ration and oil defacement. It is also required to compare the oil analysis results and the engine analysis results including inside contamination and wear condition of engine, and to consider the engine operating condition. Be sure to use Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Genuine long life coolant (LLC) 'GLASSY long life coolant (Ethyl- ene glycol type)' or 'PG GLASSY long life coolant (Non-amine type)' as coolant. When using other brand LLCs by necessity, be sure to use the LLC that meets the specification in Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. LLC shall be a homogeneous liquid. GLASSY long life coolant (Non-amine type)', be sure Engine cooling system shall not receive troubles to use the LLC which meets specification in Mitsubishi such as corrosions and precipitation products etc. By Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Chapter 6 COOLANT LLC specification LLC shall examine according to JIS K2234 section 7 (examination methods), and satisfy this specification. General matters and the sample to the examination is shown in JIS K2234. Table 6-2 LLC specification Property Standard External Not precipitation Minimum 1.112 g/cm 69.4199 lb/ft. Chapter 6 COOLANT Table 6-2 LLC specification Property Standard Aluminum ±0.60 mg/cm Cast iron ±0.30 mg/cm Steel ±0.30 mg/cm Mass change Brass ±0.30 mg/cm Test piece Solder ±0.60 mg/cm Circulation Copper ±0.30 mg/cm metallic causticity (88±3°C External of test piece after the Not corrosion on surface excluding between 190±37°F, examination.
Failure to renew LLC may cause malfunctions due to performance degradation of preventing rust and cavitation. The coolant mixed with LLC which Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Recommended expires in 2 years. Be sure to change coolant at least once every 2 years. Chapter 6 COOLANT Importance of LLC Examples of abnormali- Today's trend is toward smaller and lighter engines ties caused by LLC (amine offering greater output, lower fuel consumption and type) lower exhaust emission levels. Conditions to which engine coolant is subjected, Pitting of iron parts therefore, are becoming severer due to longer operat- Amines are generally effective in suppressing the rust.
Check the operating record of the engine to determine the most appropriate service intervals. (Feel free to consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Regarding service intervals.) Service the items at multiples of the original requirement. For example, at 1000 service hours, also service those items listed under every 250 service hours and every 50 service hours. Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE Maintenace schedule Table 7-1 Maintenace schedule Interval and Service item Page Fuel tank - Drain water (If water sedimenter is installed, drain water every 500 service hours or 1 Every 50 service hours year.) Air cleaner - Check 8-14 Solenoid fuel pump filter - Inspect and clean First 50 service hours for. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Basic engine Belt and belt tension - Inspect and Adjust If defects such as cuts or surface separations are found during inspection, replace the belt. Keep oil and grease away from the belt. They may cause the belt to slip and shorten the service life. Excessive belt tension can cause rapid wear of the alternator bearing and shorten the service life of the belt.
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Fuel system Fuel tank - Drain water When working around fuel, make sure there are no open flames, heaters or other fire hazards. Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
Do not remove the strainer when filling the fuel. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Fuel system - Bleed air When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine. Wipe off any spilled fuel completely.Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire. When cleaning or replaceing the parts of fuel system, perform air bleeding from each parts. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Water sedimenter - Bleed air 1. Loosen the fuel inlet port air vent plug of water sed- imenter. Air bleed plug 2.
Feed fuel using the solenoid fuel pump. At fuel inlet side 3. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Water sedimenter - Drain water When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine.
Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Fuel filter element (switching cock type) - Replace When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine.Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
When draining oil or changing the oil filter, wear gloves. Hot engine oil and parts may cause burns. Do not dump waste oil. It is forbidden by law. For disposal of waste oil, consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Indus- tries, Ltd. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Engine oil - Refill 1.

Make sure that the oil drain plug is tightened. Oil filler 2. Remove the oil filler cap.
Oil level gauge 3. Fill the engine oil pan with specified engine oil to the specified level. Note: Check the element of the oil filter that has been Apply engine oil removed. If metal particles are found, consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Thoroughly wipe off oil on the mounting surface of oil filter with a waste cloth. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Cooling system Coolant - Change Stand the lever to Turn the cap about Remove the radiator filler cap only after the engine the upright position half a turn has cooled to room temperature. Place a waste cloth over the cap, and loosen the cap about a half-turn or stand the lever to the upright position to release inter- nal pressure. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Cooling system - Clean Clean the cooling system when operating the engine first time, or restarting the engine after storage with coolant drained. Close coolant drain cocks and plugs. Coolant drain plug 2. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Coolant - Refill 1.
Tighten the coolant drain cocks and plugs. Remove the radiator filler cap, and pour in undilut- ed LLC. Note: Determine the amounts of LLC and water to be added by using the LLC concentration chart. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Radiator fins - Check and Clean When handling compressed air, wear safety goggles, a hardhat, gloves and other necessary protective gear. Works without wearing proper protective gear could result in serious injuries. Check the radiator fins for holes and cracks.
Mercury 6 Hp 4-stroke Carburetor
To clean the radiator fins, blow compressed air from the opposite direction of the normal air flow. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Inlet and exhaust systems Air cleaner - Check Reset button Checking procedure described below is a commonly Signal used procedure.
Some application may be equipped (red) with different air cleaner. Check the air cleaner indicator for the element clog. Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Air cleaner element - Clean, Check and Replace When handling compressed air, wear safety goggles, a dust mask, a hardhat, gloves and other necessary protec- tive gear. Works without wearing proper protective gear could result in serious injuries. Never service the air cleaner while the engine is running.
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Electrical system Battery - Inspect If battery electrolyte is spilled on your skin, flush immediately with plenty of water. If battery electrolyte enters the eyes, flush them immediately with lots of fresh water and seek medical attention at once. Do not use open flames or other fire hazards near the battery. If the alternator is dusty, blow foreign material using Alternator compressed air. Remove the belt and check that the movement is smooth when rotating the pulley by hand. Note: If the alternator is defective, consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
8-28 Alternator - Inspect 8-17. Chapter 9 LONG-TERM STORAGE Long-term storage The following describes how to store the engine in a non-operable condition for 3 months or more and in an opera- ble condition for 3 months or more. If the engine has been left unattended for 3 months or more, the internal engine parts can rust, and that may cause damage to the engine. Chapter 9 LONG-TERM STORAGE Using the engine after storage 1. Remove the cover from the engine. Connect a fully charged battery.
Remove the covers from the starters and alternator. Adjust the tension of belt. Note: Inspect and adjust V-belt tension. Refer to 'Belt and belt tension - Inspect and Adjust'. Chapter 10 TRANSPORTATION Lifting the engine Rear hanger Front hanger To lift the engine, use wire ropes, shackles and slings capable of supporting the weight of the engine.
Attach the wire rope to the hangers provided on the engine using a correct sling. Keep the engine balanced during lifting by consider- ing the engine's center of gravity. Chapter 11 TROUBLESHOOTING General precautions Contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Cautions against contamination Heavy Industries, Ltd.
For repair Dust and foreign materials are the most common service cause of rapid wear of parts. Repairing a malfunctioning engine may require special. (Refer to P8-16) Faulty battery Charge battery. Change battery. Faulty starter or starter relay Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Oil viscosity too high Use appropriate engine oil. (Refer to P5-1) Lubricating Check amount of engine oil and lubrication system. Clogged fuel filter (Refer to P8-6) Gauze filter - Clean Faulty fuel feed pump Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Fuel system Faulty fuel injection pump Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Faulty fuel injection nozzle Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Improper fuel property Check cetane index, and use appropriate fuel.
(Refer to P4-1) Faulty fuel injection timing Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Faulty fuel injection nozzle Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Fuel system Check ignition noise, exhaust smoke temperature. Remedies Improper fuel property Use appropriate fuel. (Refer to P4-1) Faulty fuel feed pump Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.

Faulty fuel injection pump Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Fuel system Faulty fuel injection nozzle Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Fuel consumption is high Table 11-6 Fuel consumption is high Cause Remedies Faulty fuel injection nozzle Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Faulty fuel injection timing Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Fuel system Improper fuel property Use appropriate fuel. Table 11-7 Engine oil consumption is high Cause Remedies Fuel system Faulty fuel injection timing Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Check oil leakage. Oil leakage to the outside of engine Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Engine oil viscosity too low Use appropriate oil viscosity.
Low coolant level Check coolant level. (Refer to P3-3) Faulty water pump operation Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Cooling sys- Faulty thermostat operation Consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Check and clean radiator and radiator filler cap. Chapter 11 TROUBLESHOOTING When fuel has run out When fuel runs out while engine is running and the engine has stopped, restart the engine as described below.
Return the starter switch to the 'OFF' position. Add fuel to the fuel tank. For filling fuel tank, refer to 'Fuel tank oil level - Check'. Chapter 12 MAIN SPECIFICATIONS Main specifications Table 12-1 Main specifications Item Specifications Engine model Type Vertical water cooled, 4 stroke cycle diesel engine No. Of cylinders - 2 cylinder in-line 3 cylinder in-line arrangement Cylinder bore × stroke φ76 × 70 mm 2.99 x 2.76 in. φ76 ×.